Completed Pneumatic Caisson Construction Projects
Bridge Foundation (overseas)
Bridge name |
Korea Yeongjong Bridge (self-anchored 3D cable suspension bridge) |
Project owner |
South Korea New Airport Expressway |
Construction period |
From June 1996 to June 1998 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 47.1 m x 18.1m Area, 852 m2 |
Maximum air pressure |
0.36 MPa |
Bottom supporting soil |
Hard rock |
- Steel shells were tugged by a floating crane vessel with capacity of 300 tons and lifted in one piece at the site due to difficult working conditions.
1.5 km away from shore
Tidal variation, 8.5 m (max 10.0 m)
Tidal current, 2.15 m/s
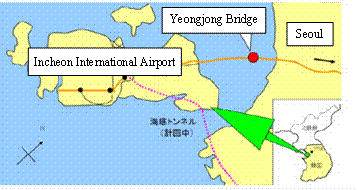
Project location

Steel shell tugged by floating crane

Construction work in progress
Bridge Foundation (in Japan)
Bridge name |
Rainbow Bridge (Odaiba side) |
Project owner |
Metropolitan Expressway Co., Ltd. |
Construction period |
From November 1986 to July 1991 (through construction of anchor block) |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 45.1 m x 70.1 m (anchorage) Area, 3,157 m2 Rectangular, 21.1 m x 49.1 m (main tower) Area, 1,031 m2 |
Maximum air pressure |
0.40MPa |
Bottom supporting soil |
Hardpan (soft rock) |
- When constructed, it was the world's largest foundation by pneumatic caisson construction.
- Steel shells were tugged by vessel.
- Constructed near the third and sixth Daibas, which are designated important cultural properties.

Over view of Rainbow Bridge
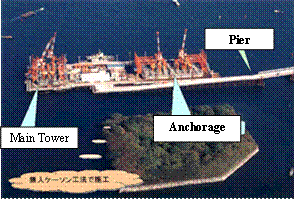
Construction work in progress
Bridge name |
Meiko Nishi Ohashi |
Project owner |
Japan Highway Public Corporation |
Construction period |
From November 1993 to August 1996 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 40.1 m x 25.1 m Area, 1,006 m2 |
Maximum air pressure |
0.40MPa |
Bottom supporting soil |
Sand layer |
- The deep well method was adopted to reduce the working air pressure during Phase 1 construction.
- The deep pneumatic caisson method with a helium mixed gas respiration system was adopted due to consideration of the construction site surroundings in Phase 2.
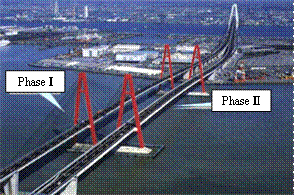
Overview of Meiko Nishi Ohashi and
Ise expressway

Construction work in progress during Phase 1
Sewage Pump Station
Building name |
Nishi Nippori Line Pump Station at Higashi Ogu Purification Center |
Project owner |
Bureau of Sewerage, Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
Construction period |
From August 2006 to May 2010 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 62.1 m x 77.9 m Area, 4,838 m2 |
Sinking depth |
43.7 m |
- This is the world's largest pneumatic caisson structure. The construction area was 1.5 times larger than the Rainbow Bridge anchorage foundation.

Construction work in progress
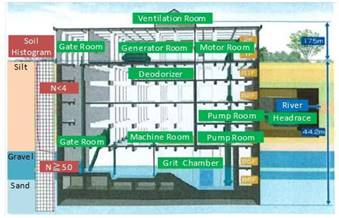
Structure schematic plan
Building name |
Shinmei Pump No. 2 Station |
Project owner |
City of Chiba |
Construction period |
From August 2004 to January 2008 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 17.6 m x 33.1 m Area, 581 m2 |
Sinking depth |
27.4 m |
- Constructed in the narrow space between residences and the nearby Keisei Electric Railway and East Japan Railway.
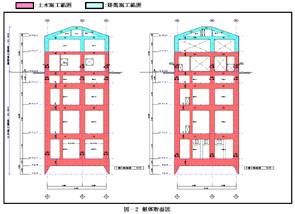
Structural plan
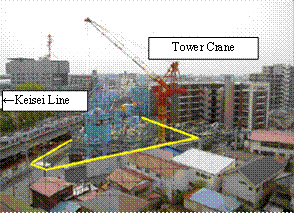
Construction work in progress
Underground Regulating Reservoir
Structure name |
Regulating reservoir of Enkaido Area |
Project owner |
City of Ichinomiya, Aichi Prefecture |
Construction period |
From November 2002 to July 2003 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Round, 37.1 m Area, 1,081 m2 |
Sinking depth |
17.3 m |

Concept drawing of completed reservoir

Construction work in progress
Structure name |
Shinke Regulating Reservoir of Neyagawa, Grade one river |
Project owner |
Osaka Prefecture |
Construction period |
From December 2005 to September 2008 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Round, 50.6 m x 49.9 m Area, 2,015 m2 |
Sinking depth |
47.9 m |
- This is the world's largest round pneumatically constructed caisson.
Structural plan

Construction work in progress
Launching and Reception Vertical Shaft
Structure name |
Launching Vertical Shaft of Second Tameike Sewage Line |
Project owner |
Bureau of Sewerage, Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
Construction period |
From July 2008 to August 2010 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 19.7 m x 23.6 m Area, 465 m2 |
Sinking depth |
54.35 m |
- Due to massive nearby residences, countermeasures for mitigating impacts to the surrounding neighbors' environment were implemented, such as covering the construction site with sound-proofing panels.
- A helium mixed gas respiration system was adopted due to the depth of the underground construction.

Installed sound-proofing panels

Interior view of sound-proofing panels
Project name |
Sibajima Launching Vertical Shaft Construction Work for Water Service Pipe Renovation Work of Central and Western Area, Horie Line and others |
Project owner |
Osaka City Waterworks Bureau |
Construction period |
From January 1999 to November 2000 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Round,17.6 m Area, 243 m2 |
Sinking depth |
63.5 m |
- This was a large, deep pneumatic caisson construction project inside an existing water treatment plant.
- A helium mixed gas respiration system was adopted.
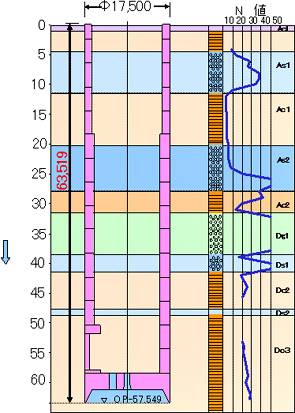
Soil boring log

Construction work in progress
Railway and Road Tunnel
Project name |
New Connecting Road Construction Work between Kitayono and Omiya of JR East Saikyo Line |
Project owner |
JR East, consigned by Metropolitan Expressway Co., Ltd . |
Construction period |
From September 2000 to February 2002 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Variable shape, 46.0 m x 24.8 m Area, 1,038 m2 |
Sinking d epth |
35.8 m |
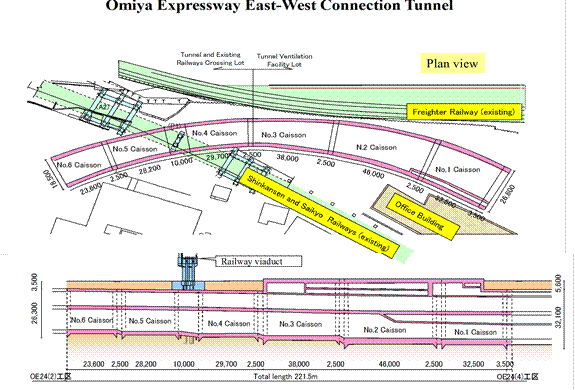
General plan
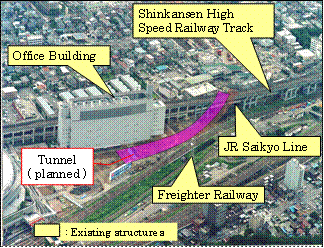
Overview before construction

Construction work in progress
Project name |
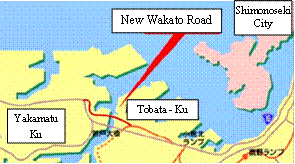
Shin-Wakato Road Tunnel |
Project owner |
Kyushu Regional Development Bureau of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism |
Construction period |
From February 2005 to March 2006 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 42.5 m x 35.05 m (U4); Area, 1,488 m2 Variable shape, 35.0 m x 35.0 m, 17.0 m x 23.6 m (U5); Area, 1,723 m2 |
Sinking depth |
13.4 m (U4), 13.9 m (U5) |
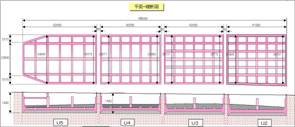
General plan
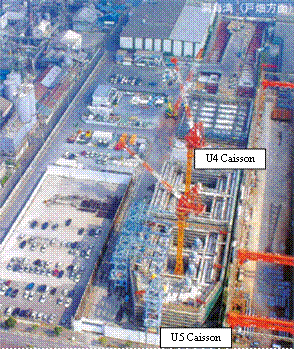
Construction work in progress
Underground Building Structure
Building name |
Underground parking in front of Shizuoka Station |
Project owner |
Chubu Regional Development Bureau of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism |
Construction period |
From March 2000 to March 2003 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 46.1 m x 63.7 m Area, 2,937 m2 |
Sinking depth |
21.9 m |
- The project objective was to solve a parking shortage.
- Caisson construction occurred in the narrow space between Shizuoka Shinkansen Station and National Road Route No. 1.
- Completed floor area is around 3,000 m2.

Project plan

Construction work in progress
Slim Caisson
Bridge name |
Shin-Shonan Oohashi Foundation work for bridge over the estuary of Sagami River |
Project owner |
Kanto Regional Development Bureau of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism |
Construction period |
From December 2005 to March 2006 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Round, 6.5 m Area, 33.18 m2 |
Sinking depth |
45.62 m |
- The slim caisson method was adopted due to the small- diameter caisson.
- A helium mixed gas was applied at first time in the slim caisson method due to the great deep and high air pressure. (Air pressure at actual work site was 0.434 MPa.)

General plan

Construction work in progress
Project name |
Tosu-Mishima and other viaducts of Kyushu Shinkansen Line |
Project owner |
Kyushu Shinkansen Construction Bureau, Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency |
Construction period |
From March 2004 to July 2007 |
Shape of caisson structure Sinking depth |
Round, 5.0 m; area, 19.63 m2 (4 pieces) Round, 5.0 m; area, 19.65 m2 (1 piece) 38.0 m (4 pieces), 30.5 m (1 piece) |
- The slim caisson method was adopted for the small-diameter caissons.
- The caissons were constructed near the JR Kyusyu Kagoshima Main Line while it was in operation, and the minimum distance from the center of the railway track to the centerof the caissons was 6,184 mm.
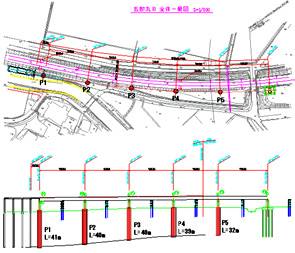
General plan

Construction work in progress
Eco-Caisson
Project name |
Minami Tanaka Tunnel Construction of Tokyo Circle Line No. 8 |
Project owner |
Bureau of Construction, Tokyo Metropolitan Government |
Construction period |
From January 2004 to November 2004 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Rectangular, 19.9 m x 30.0 m Area, 597 m2 |
Sinking depth |
13.4 m |
- Countermeasures for conservation of underground water flow were implemented.
- The construction area was between Nerima-ku and Itabashi-ku.
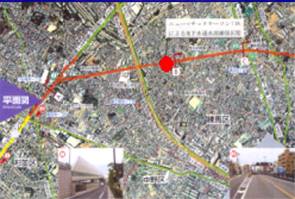
Project overview

Construction work in progress
Project name |
Experimental Construction work at Kokubun Area of Tokyo Outer Ring Expressway |
Project owner |
Tokyo Outer Ring Construction Office, NEXCO East |
Construction period |
From June 2006 to July 2008 |
Shape of caisson structure |
Variable shape, 28.8 m x 60.0 m Area, 1,615 m2 |
Sinking depth |
17.1 m |
- Countermeasures for conservation of underground water flow were implemented.
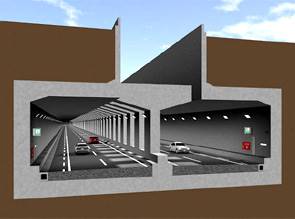
Concept drawing of completed project

Construction work in progress







